Illustration of the Firewall
A fire wall is a system or device that allow network traffic that is considered safe for through traffic and prevent an insecure network. Generally, a wall-fire applied in a dedicated machine, running on the gateway (gateway) between the local network and other networks. Wall-fire is generally also used to control access to anyone who has access to a private network from outside parties. Today, the term firewall became prevalent that the term refers to systems that manage communication between two different networks. Given today many companies that have access to the Internet and also of course the network incorporated in it, then the protection of digital capital of the company from attacks by hackers, pemata-eye, or other data thieves, into nature.
The types of firewalls
taxonomy Firewall
Firewalls are divided into two types, namely as follows
A. Personal Firewall : Personal Firewall designed to protect a computer connected to the network from unwanted access. This type of firewall lately evolved into a collection of programs that aim to secure the computer in total, with the addition of some additional security features such protection devices against viruses, anti-spyware, anti-spam, and others. Even some other firewall product comes with a network security breach detection function (Intrusion Detection System). Examples of this type of firewall is the Microsoft Windows Firewall (which have been integrated in the operating system Windows XP Service Pack 2, Windows Vista and Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 1), Symantec Norton Personal Firewall, Kerio Personal Firewall, and others. Personal Firewall is generally only has two main features, namely the Packet Filter Firewall and Stateful Firewall.
Firewall functions
Basically, a firewall can do the following things:
a. Regulate and control the network traffic
The first function that can be done by the firewall is a firewall should be able to regulate and control the network traffic is allowed to access the private network or computer protected by a firewall. Firewalls do so, by conducting inspections of packages and monitor the connection is made, then do the screening (filtering) of connections based on packet inspection and connection.
The first function that can be done by the firewall is a firewall should be able to regulate and control the network traffic is allowed to access the private network or computer protected by a firewall. Firewalls do so, by conducting inspections of packages and monitor the connection is made, then do the screening (filtering) of connections based on packet inspection and connection.
- Package inspection process
Packet inspection ('packet inspection) is a process performed by the firewall to' block 'and process the data in a packet to determine that the packet was permitted or denied, based on access policies (access policy) is applied by an administrator. Firewall, before making a decision whether to reject or accept the communication from the outside, he must perform inspections of each packet (either an incoming or outgoing) at each interface and compare it to the list of access policies. Packet inspection can be done by looking at the following elements, when determining whether to reject or accept the communication:
Packet inspection ('packet inspection) is a process performed by the firewall to' block 'and process the data in a packet to determine that the packet was permitted or denied, based on access policies (access policy) is applied by an administrator. Firewall, before making a decision whether to reject or accept the communication from the outside, he must perform inspections of each packet (either an incoming or outgoing) at each interface and compare it to the list of access policies. Packet inspection can be done by looking at the following elements, when determining whether to reject or accept the communication:
• The IP address of the computer source
• The port on the source computer source
• The IP address of the destination computer
• The destination port on the destination computer data
• IP Protocol
• Information headers stored in the package
• The port on the source computer source
• The IP address of the destination computer
• The destination port on the destination computer data
• IP Protocol
• Information headers stored in the package
- Connection and Connection State
In order for two hosts TCP / IP can communicate with each other, they must each make a connection between each other. This connection has two purposes:
In order for two hosts TCP / IP can communicate with each other, they must each make a connection between each other. This connection has two purposes:
1. Computers can use that connection to identify itself to other computers, which assured that the other systems that do not make the connection can not transmit data to the computer. Firewalls can also use the connection information to determine what connections are allowed by the policy of access and use it to determine whether the data packet will be accepted or rejected.
2. Connection is used to determine how these two hosts will communicate with each other (whether by using a connection-oriented connection, or connectionless).
Both of these goals can be used to determine the state of the connection between two hosts, as well as the way humans converse. If Amina Amir asked about something, then Aminah will respond with appropriate answers to the questions posed by the Amir; At the time of asking question to Aminah Amir, Amir's state of the conversation is awaiting a response from Aminah. Communication in the network also follows a similar way to monitor the state of communication conversations that occur.
Both of these goals can be used to determine the state of the connection between two hosts, as well as the way humans converse. If Amina Amir asked about something, then Aminah will respond with appropriate answers to the questions posed by the Amir; At the time of asking question to Aminah Amir, Amir's state of the conversation is awaiting a response from Aminah. Communication in the network also follows a similar way to monitor the state of communication conversations that occur.
Illustration of a conversation between two hosts
Firewalls can monitor the connection state information to determine whether he would allow the network traffic. Generally this is done by maintaining a connection state table (in terms of firewall: state table) which monitor the state of all communications that pass through the firewall. By monitoring the state of this connection, the firewall can determine whether the data that passes through the firewall is "expected" by the destination host, and if yes, aka permits. If the data that passes through the firewall does not match the connection state of the connection state is defined by the table, then the data will be rejected. This is commonly referred to as Stateful Inspection.
Stateful Packet Inspection
When combining a stateful inspection firewall with packet inspection, then the firewall is called a Stateful Packet Inspection (SPI). SPI packet inspection is a process that is not done using the package structure and the data contained in the package, but also in what circumstances hosts communicate with each other is located. SPI allows the firewall to do the screening is not only based on the contents of the package, but also based on a connection or connection state, which would cause the firewall has the ability to more flexible, manageable, and has the scalability in terms of screening is high.
When combining a stateful inspection firewall with packet inspection, then the firewall is called a Stateful Packet Inspection (SPI). SPI packet inspection is a process that is not done using the package structure and the data contained in the package, but also in what circumstances hosts communicate with each other is located. SPI allows the firewall to do the screening is not only based on the contents of the package, but also based on a connection or connection state, which would cause the firewall has the ability to more flexible, manageable, and has the scalability in terms of screening is high.
One of the benefits of SPI as compared to regular inspection package is that when a connection has been recognized and permitted (of course after the inspection), generally a policy (policy) is not required to allow communications replies because the firewall know what response is expected to be received. This allows inspection of the data and commands contained in a data packet to determine whether a connection is allowed or not, then the firewall will automatically monitor the conversations and dynamically allow traffic in accordance with the circumstances. This is a significant increase when compared with normal packet inspection firewall with. Moreover, this process is completed without the need to define a policy to allow the response and subsequent communications. Most modern firewalls have support this function.
b. Perform authentication on access
The second fundamental functions of a firewall is a firewall can perform authentication for access.
Protocol TCP / IP is built with the premise that the protocol allows open communication. If two hosts know each IP address to each other, then they are allowed to communicate with each other. In the early development of the Internet, this may be regarded as a blessing. But today, when more and more connected to the Internet, maybe we do not want anyone who can communicate with the system we have. Therefore, the firewall is equipped with authentication function by using multiple authentication mechanisms, as follows:
The second fundamental functions of a firewall is a firewall can perform authentication for access.
Protocol TCP / IP is built with the premise that the protocol allows open communication. If two hosts know each IP address to each other, then they are allowed to communicate with each other. In the early development of the Internet, this may be regarded as a blessing. But today, when more and more connected to the Internet, maybe we do not want anyone who can communicate with the system we have. Therefore, the firewall is equipped with authentication function by using multiple authentication mechanisms, as follows:
• Firewalls can request input from the user regarding the user name (user name) and password (password). This method is often referred to as extended or xauth authentication. Using xauth users are trying to make a connection will be asked to input the name and password before being allowed by the firewall. Generally, after the connection is allowed by the security policy in the firewall, the firewall does not need to input a password and fill in his name, unless the connection is lost and the user tries to connect him back.
• The second method is to use digital certificates and public key. The advantages of this method compared with the first method is the authentication process can occur without user intervention. In addition, this method is much faster in order to authenticate. However, this method is more complicated implementation because it requires many components such as public key infrastructure implementations.
• The next method is to use Pre-Shared Key (PSK) or a key that has been notified to the user. When compared with digital certificates, PSK diimplenentasikan easier because more simple, but prostitutes also allow the authentication process occurs without user intervention. By using PSK, each host will be given a predetermined key is then used for authentication. The weakness of this method is the key PSK is rarely updated and many organizations often use the same key to connect to hosts that are on long-distance, so this is the same as undermining the authentication process. In order to achieve a high degree of security, generally some organizations also use a combination of methods with xauth PSK or PSK with a digital certificate.
c. Protect the resources in the private network
One task of a firewall is to protect resources from threats that might come. This protection can be obtained by using several regulations setting access (access control), the use of SPI, application proxies, or a combination thereof to prevent the protected host can be accessed by the host of suspicious or suspicious network traffic. Even so, the firewall is not the only method of protection to resources, and entrust the protection of resources from the threat to the firewall exclusively is one fatal flaw.
One task of a firewall is to protect resources from threats that might come. This protection can be obtained by using several regulations setting access (access control), the use of SPI, application proxies, or a combination thereof to prevent the protected host can be accessed by the host of suspicious or suspicious network traffic. Even so, the firewall is not the only method of protection to resources, and entrust the protection of resources from the threat to the firewall exclusively is one fatal flaw.
If a host is running a particular operating system that has not yet patched security holes connected to the Internet, the firewall may not be able to prevent the exploitation of the host by other hosts, especially if the exploit is using the traffic has been allowed by the firewall (in configuration). For example, if a packet-inspection firewall allows HTTP traffic to a web server that runs a web service that has security holes that have not patched, then a user is "fun" can only make the exploit to undermine the web server because the web server concerned have not yet patched security holes. In this example, the web server eventually lead to the protection offered by the firewall becomes useless. This is caused by a firewall can not distinguish between suspicious HTTP request or not. Moreover, if the firewall is not an application proxy. Hence, protected resources must be maintained by filling of the security holes, but of course protected by a firewall.
How it Works Firewall
1. Packet-Filter Firewall
Examples of access arrangements (access control) is implemented in the firewall
In its simplest form, a firewall is a router or a computer equipped with two NICs (Network Interface Card, network interface card) that is able to do the screening or filtering of incoming packets. Devices of this type generally referred to as packet-filtering routers.
This type of firewalls work by comparing the source address of these packets by access control policies that are listed in the Access Control List firewall, the router will try to decide whether to forward the incoming packet to its destination or stop it. In a simplified form again, the firewall only perform testing of the IP address or domain name is the source of the packet and will determine whether to continue or reject the package. However, packet-filtering router can not be used to provide access (or reject) by using a base rights owned by the user.
This type of firewalls work by comparing the source address of these packets by access control policies that are listed in the Access Control List firewall, the router will try to decide whether to forward the incoming packet to its destination or stop it. In a simplified form again, the firewall only perform testing of the IP address or domain name is the source of the packet and will determine whether to continue or reject the package. However, packet-filtering router can not be used to provide access (or reject) by using a base rights owned by the user.
The workings of packet filter firewalls
Packet-filtering router can also be configured to stop some types of network traffic and of course allow it. Generally, this is done by enabling / disabling the TCP / IP in the firewall system. For example, port 25 is used by the protocol SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) is generally left open by several firewall to allow electronic mail from the Internet into the private network, while other ports such as port 23 is used by the Telnet protocol can be disabled to prevent users Internet to access services available in the private network. Firewalls can also provide a kind of exception (exception) so that multiple applications can pass through the firewall. By using this approach, the security will be stronger but have significant drawbacks that the complexity of firewall configuration: a list of the Access Control List firewall will enlarge as many IP addresses, domain names, or port that is inserted into it, but of course also exceptions that apply.
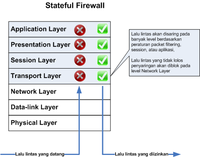
2. Stateful Firewall
The workings of Stateful Firewall
B. Network Firewall :''Network Firewall designed to protect the overall network from various attacks. Generally found in two forms, namely a dedicated device or as a software installed in a server. Examples of this firewall is Microsoft Internet Security and Acceleration Server (ISA Server), Cisco PIX, Cisco ASA, IPTables in the operating system GNU / Linux, pf in BSD Unix family of operating systems, and sunscreen of Sun Microsystems, Inc.. bundled in the Solaris operating system. Network Firewalls in general has several key features, namely what is owned by a personal firewall (packet filter firewalls and stateful firewalls), Circuit Level Gateway, Application Level Gateway, as well as NAT Firewall. Network Firewalls generally are transparent (not visible) of users and uses routing technology to determine which packets are allowed, and where the package will be rejected.
1. Circuit Level Gateway
The workings of circuit-level firewall
Another type of firewall is the Circuit-Level Gateway, which is usually a component of a proxy server. This type of firewall operates at a higher level in the seven layer OSI reference model (working at the session layer / session layer) than the Packet Filter Firewall. This modification makes the firewall of this type are useful in order to conceal information about the network being protected, even if the firewall does not perform filtering on individual packages flowing in the connection.
By using this type of firewall, the connection that occurs between the user and the network was hidden from the user. Users will be confronted directly with the firewall during the process of making connections and firewalls also will establish a connection with network resources that would be accessed by the user after changing the IP address of the packet transmitted by the two parties. This resulted in a virtual circuit (virtual circuit) between users and network resources that he had access.
Firewalls are considered more secure than the Packet-Filtering Firewall, because external users can not see the internal network IP addresses in the packets that he receives, but the IP address of the firewall. Popular protocol used as a Circuit-level gateway is SOCKS v5.
By using this type of firewall, the connection that occurs between the user and the network was hidden from the user. Users will be confronted directly with the firewall during the process of making connections and firewalls also will establish a connection with network resources that would be accessed by the user after changing the IP address of the packet transmitted by the two parties. This resulted in a virtual circuit (virtual circuit) between users and network resources that he had access.
Firewalls are considered more secure than the Packet-Filtering Firewall, because external users can not see the internal network IP addresses in the packets that he receives, but the IP address of the firewall. Popular protocol used as a Circuit-level gateway is SOCKS v5.
2. Application Level Firewall (application proxy or application level gateway)
The workings of Aplication Level Firewall
Another type of firewall is the Application Level Gateway (or Application-Level Firewall or often referred to as Proxy Firewall), which is generally also a component of a proxy server. This firewall does not allow incoming packets to pass through the firewall directly. However, the proxy application running in a computer that is running the firewall will forward the request to the services available in the private network and then forwards the response of the requests to the computer making the request was first located in an insecure public network.
Generally, a firewall of this type will perform prior to user authentication before allowing users to access the network. In addition, these firewalls also implement mechanisms of auditing and recording (logging) as part of security policy implementation. Application Level Firewalls also usually require some configuration that is imposed on the user to allow a client machine in order to function. For example, if an FTP proxy configured on an application layer gateway, the proxy can be configured to mengizinlan some FTP commands, and rejecting several other commands. This species is most often implemented in SMTP proxy so they can receive electronic mail from the outside (without revealing internal e-mail address), and forward e-mails to the e-mail server in the network. However, because of the more complex processing, this type of firewall requires a computer that is configured as an application gateway has a high specification, and of course much slower than the packet-filter firewall.
Generally, a firewall of this type will perform prior to user authentication before allowing users to access the network. In addition, these firewalls also implement mechanisms of auditing and recording (logging) as part of security policy implementation. Application Level Firewalls also usually require some configuration that is imposed on the user to allow a client machine in order to function. For example, if an FTP proxy configured on an application layer gateway, the proxy can be configured to mengizinlan some FTP commands, and rejecting several other commands. This species is most often implemented in SMTP proxy so they can receive electronic mail from the outside (without revealing internal e-mail address), and forward e-mails to the e-mail server in the network. However, because of the more complex processing, this type of firewall requires a computer that is configured as an application gateway has a high specification, and of course much slower than the packet-filter firewall.
3. NAT Firewall
NAT (Network Address Translation) Firewall automatically provides protection to systems that are behind a firewall because NAT Firewall to allow incoming connections only from computers that are behind a firewall. The purpose of NAT is to perform multiplexing of traffic from internal network to then present it to the wider network (MAN, WAN or Internet) as if the package is coming from an IP address or multiple IP addresses. NAT Firewalls create a table in memory that contains information about the connection as seen by the firewall. This table will map the internal network address to external address. The ability to put the whole network behind an IP address based on the mapping of ports in NAT firewall.
Another type of firewall
- Virtual Firewall
Virtual Firewall is the name for several logical firewalls that are in a physical device (computer or other firewall software). This arrangement allows multiple networks to be protected by a firewall that is running a unique security policy which is also unique, simply by using a single device. By using a firewall of this type, an ISP (Internet Service Provider) can provide firewall services to its customers, thus securing their network traffic, using only one device. This is clearly a significant cost savings, although this type of firewall is only available on top-class firewall, such as the Cisco PIX 535.
- Transparent Firewall
Transparent Firewall (also known as a bridging firewall) is not a pure firewall, but he is just a derivative of the stateful firewall. Other than the firewall-firewall that operates at the IP layer to the top, transparent layer firewalls work on the Data-Link Layer, and then he monitors the layers above it. In addition, the transparent firewall can also perform what can be done by the packet-filtering firewall, such as stateful firewall and are not visible to the user (that's why, he referred to as Transparent Firewall).
In essence, the transparent firewall works as a bridge that served to filter the network traffic between two network segments. By using the transparent firewall, the security of a network segment can be strengthened, without having to apply NAT Filter. Transparent Firewall offers three advantages, namely as follows:
In essence, the transparent firewall works as a bridge that served to filter the network traffic between two network segments. By using the transparent firewall, the security of a network segment can be strengthened, without having to apply NAT Filter. Transparent Firewall offers three advantages, namely as follows:
• Configuring an easy (and even some products claim to be "Zero Configuration"). This is because the transparent firewall is directly connected with the network who want diproteksinya, with or without modifying slightly modifying the firewall configuration. As he worked on data-link layer, changing the IP address was not required. Firewalls can also be configured to perform segmentation of a network between the network subnet that has a low security and high security, or can also be to protect a host, if necessary.
• The high performance. This is caused by a firewall running in the data-link layer is simpler than the firewall running in the higher layers. Because the work is more modest, then the processing needs of even smaller compared with the firewall running on a high layer, and finally performance ditunjukannya even higher.
• Not visible to the user (stealth). This is because the Transparent Firewall works on data-link layer, and does not require an assigned IP address for him (except for management to it, if indeed the type of managed firewall). Therefore, the transparent firewall can not be seen by the attackers. Because they can not be achieved by the attacker (it has no IP address), the attacker was not able to attack him.




















0 comments:
Post a Comment